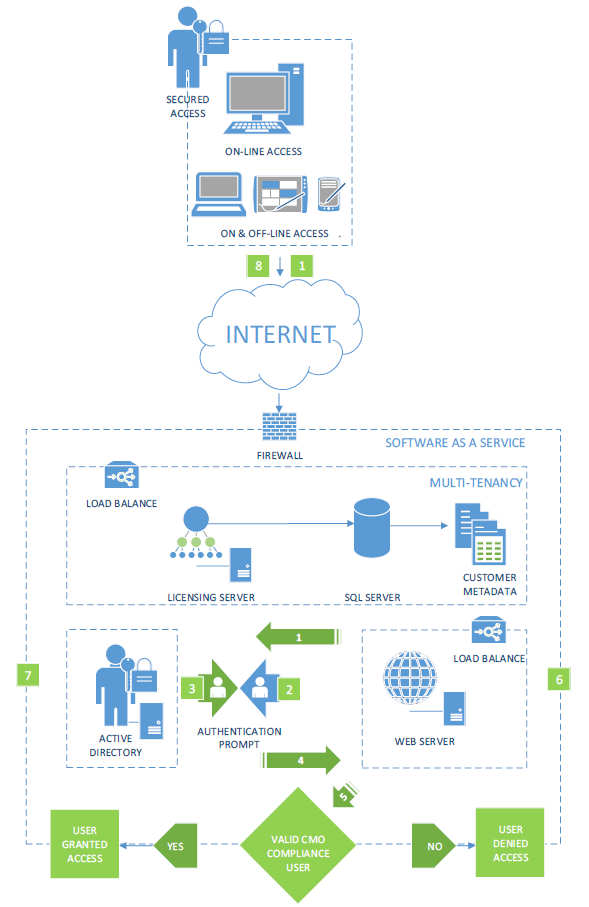
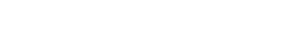Authentication
A wide variety of security access options are available to clients, using a combination of CMO COMPLIANCE-specific configurations and external software options, such as IIS.
IIS Authentication
IIS provides seamless integration with Active Directory including Active Directory Federation Services which enables users to collaborate across organizational boundaries and easily access applications on public or private clouds whilst maintaining application security, as well as providing options like SSL and integration with third party authentication mechanisms. Integrated Authentication is the typical method, but BASIC Authentication allows for a wider range of choices.
The CMO COMPLIANCE software provides two simple options to complement this: controlling how users can log on and log off, and using concepts such as the Default (generic) User. During the deployment phase, we will work with the client to identify the most appropriate configuration. This is depicted in the diagram below:
Automatic Logon (Single Sign On)
IIS Integrated Authentication
CMO COMPLIANCE allows for Integrated Auto logon (Single Sign On).
The steps for this process are:
- The user accesses the web page being serviced by IIS.
- IIS collects the user details and passes them to the Active Directory for authentication.
- If the user is a valid Active Directory user, Active Directory returns a positive result and goes to step 4. If no user exists, access is denied.
- IIS redirects traffic to the application.
- Depending on whether the user exists in CMO COMPLIANCE, they will either be granted access as a defined user, or granted access as a default or generic user.
- CMO COMPLIANCE passes the traffic back to IIS.
- IIS returns the traffic to the browser.
For Auto logon to function correctly: All users must be internal (LAN based users). Power Users are defined in the system, but other users are logged on as such, with a limited set of rights (for example, the ability to complete actions).
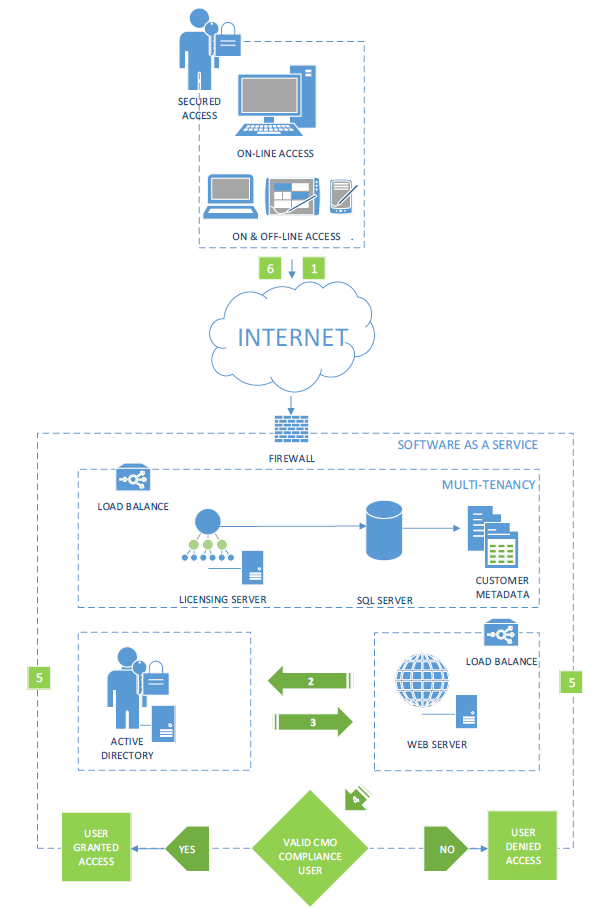
IIS Basic Authentication
CMO COMPLIANCE allows for BASIC Auto logon (Single Sign On). This may be the preferred option if users:
- Are accessing an externally facing web site
- Are sharing a PC but need to maintain separate access to the CMO COMPLIANCE application
- Log-on to another type of authentication system (e.g. Novell) so do not have a valid Active Directory token, but accounts are replicated in Active Directory.
It is similar to the previous integrated model with the following exceptions:
- The user accesses the web page being serviced by IIS.
- The user is prompted for credentials.
- IIS collects the user details and passes them to the Active Directory for authentication. SSL is used to maintain security.
- If the user is a valid Active Directory user, Active Directory returns a positive result and goes to step 4. If no user exists, access is denied.
- IIS redirects traffic to the CMO COMPLIANCE.
- Depending on whether the user exists in CMO COMPLIANCE, they will either be granted access as a defined user, or granted access as a default or generic user.
- CMO COMPLIANCE passes the traffic back to IIS.
- IIS returns the traffic to the browser.
IIS or Integrated/BASIC Authentication Model (Options): Options within the CMO COMPLIANCE application can be used to provide a greater level of security if desired are: Disable Default User. This would mean that ONLY defined users in CMO COMPLIANCE, who also have an Active Directory account, would be able to gain access to the system.
User Profiles and Access
Users are stored in the database. When a user uses the system and opens a session, profile values are also cached.
When a user (authenticated or unauthenticated) logs onto CMO COMPLIANCE, the system retrieves the profile values and caches it for the session. The cache is maintained for that session until the user logs out and closes the browser.
When a user accesses List Views, or uses forms that make use of user profile defaults, the values are retrieved from the cache.
When a user accesses the My Profile form, the system retrieves the values from the database. If the user makes a change to the profile values and saves, then the cache is updated. Note that if the user saves the My Profile form without making any changes, then the cache is not updated, as the record is not updated.
Most users only need access to the browser-based web application. Power Users, Field Users and End Users typically access different modules, which are configurable on a role by role basis from the Business Rules engine.
| User Type | Function | Access |
| End Users | Viewing and reporting on information, as well as responding to and closing out actions and issues | Browser |
| Field Users | Entering data into forms (assessments, audits, inspections and other data collection forms but excluding incident forms and actions) | Browser |
| Power Users | Maintenance and management of content and solution including reporting & analysis. | Browser |